Introduction
Ibrutinib was the first FDA-approved drug for patients (pts) with relapsed or refractory (R/R) marginal zone lymphomas (MZL), based on a phase 2 trial showing an overall response rate (ORR) of 58%, a median progression-free survival (PFS) of 15.7 months (mo) and an acceptable safety profile (Noy 2021). However, accelerated approval was voluntarily withdrawn in the US in April 2023, while it was never released by EMA. Currently, very few real world data about ibrutinib or other BTK inhibitors are available, and none from European countries.
Methods
Since November 2020 ibrutinib was available in Italy for the treatment of R/R MZL based on 648/96 Italian national law. We designed a retrospective multicentre study with the aim to evaluate efficacy and safety of ibrutinib administered until progression or unacceptable toxicity in pts with R/R MZL of either splenic, nodal, extranodal or disseminated subtype (SMZL, NMZL, EMZL, dissMZL). The study was approved by the IRB of the 19 participating centers. All pts signed informed consent. The primary endpoints were ORR and PFS.
Results
We enrolled 79 pts (45 males), including 48 SMZL, 14 NMZL, 12 EMZL and 5 dissMZL. Median age was 74 years (42-88). Median number of prior therapies was 1 (1-5). Rituximab monotherapy was the only prior line in 7 pts (9%), while 72 (91%) received at least 1 prior immuno-chemotherapy regimen (BR in 74%). Sixteen pts (20%) were primary refractory, 37 (47%) were classified as POD24 and 21 (27%) were refractory to the last therapy. TP53 deletion or mutation was detected in 10/21 available samples from SMZL cases (48%).
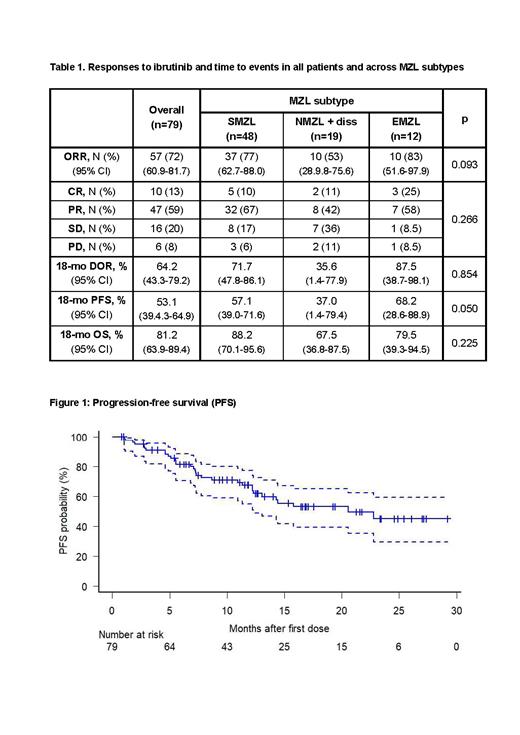
Median duration of drug exposure was 10.6 mo (95% CI 1.1-27.6). ORR was 72% (Tab 1), including 10 pts (13%) achieving a complete response (CR) and 47 (59%) a partial response (PR) (Tab 1). Median time to initial response was 3.4 mo (95% CI 0.9-10.5) and median time to best response was 6.1 mo (95% CI 1.6-16.8). NMZL or dissMZL sutype (OR 3.3, p=0.05) and pre-ibrutinib ECOG >1 (OR 8.2, p=0.008) independently predicted probability of non-response. At a median follow-up of 13.4 mo (95% CI 1.9-29.6), 29 pts progressed, including 12 responders. Median PFS was 20.5 mo (95% CI 12.3-NR, Fig 1), while median duration of response (DOR) among 57 responders was not reached (estimated 18-mo DOR 64.2%, 95% CI 43.3-79.2). None of the pts who achieved CR progressed, compared with 12/47 of those who achieved PR (18-mo DOR 100% vs 54.5%, p=0.051). At Cox regression multivariate analysis, pre-ibrutinib ECOG >1 (HR 2.09, 95% CI 1.19-3.67, p=0.01), elevated LDH (HR 2.56, 95% CI 1.13-5.79, p=0.024) and NMZL or dissMZL subtypes (HR 3.46, 95% CI 1.57-7.63, p=0.002) were associated to a worst PFS. Interestingly, pre-ibrutinib MZL-IPI,including the latter two factors plus platelet count <100 x 10 9/l, Hb <12 g/dl and absolute lymphocytes count <1 x 10 9/l ( Luminari ICML23), significantly predicted distinct PFS according to low (0, n=6, 8%, 18-mo PFS 100%), intermediate (1-2, n=50, 63%, 18-mo PFS 59%) and high risk classes (≥3, n=23, 29% 18-mo PFS 26%) (p=0.011). POD24, primary refractoriness, refractoriness to last therapy number and types of prior lines had no influence on PFS. TP53 mutation or deletion resulted significantly associated to inferior PFS in SMZL cases (p=0.015).
Overall, 32 pts (40.5%) discontinued ibrutinib, 11 for adverse events (AEs) and 21 for progressive disease (PD). Hematologic AEs were reported in 13 pts, including grade (Gr) 3-4 in 8, 10% (anemia in 4, thrombocytopenia in 3 and neutropenia in 1), while extra-hematologic AEs in 39 (49%) (Gr 3-5 in 15, 19%). The most common AEs were atrial fibrillation (n=8, 10%), bleeding (n=7, 9%), rash (n=6, 8%), diarrhea in 5 (6%), and infections (n=12, 15%), which included 3 Gr 3-4 (COVID-19, pneumonia, sepsis) and 4 Gr 5 events (septic shock in 2, aspergillosis and pneumonia). Histologic transformation was detected in 8 pts (10%). A post-progression therapy was initiated in 23 pts, resulting in ongoing CR/PR in 15. Overall, 11 pts died (6 due to PD, 4 infections, 1 suicide), with a 18-mo overall survival (OS) of 81.2% (95% CI 63.9-89.4). Not achieving ORR significantly predicted worst OS (HR 6.43, 95% CI 1.87-22.09, p=0.003).
Conclusions
Our data confirmed that ibrutinib is associated with high ORR and durable disease control in R/R MZL in real life. Toxicity was similar to what previously reported in the registration phase 2 study in R/R MZL and in other histologies. Careful attention to infectious toxicity is advised.
OffLabel Disclosure:
Nassi:Eli Lilly: Speakers Bureau; EUSApharma: Speakers Bureau; Incyte: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Takeda: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Kiowa Kirin: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Speakers Bureau; Roche: Consultancy. Arcari:Janssen, Abbvie, Takeda, Servier: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau. Vitale:Janssen, Abbvie, Astra-Zeneca, Beigene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau. Annibali:Amgen: Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Speakers Bureau; Takeda: Speakers Bureau. Passamonti:Roche: Consultancy; Abbvie: Consultancy, Honoraria; BMS: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis, GSK, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Sierra Oncology, AbbVie, Janssen, Roche, AOP Orphan, Karyopharm, Kyowa Kirin, MEI, Sumitomo: Honoraria.
Ibrutinib is not licensed in Europe for the treatment of relapsed or refractory marginal zone lymphomas. however it was available in Italy according to the 648/96 Italian national law since November 2020.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal